个人介绍
本人国内985、211毕业硕士研究生,熟练掌握ORACLE,PYTHON,MATLAB,C++等语言,对算法、数据库方面有一定的研究与了解。一方面,本人比较擅长解决优化方面,尤其是关于进化算法的问题。另一方面,本人有2年多的数据库运维方面学习工作经历,对数据库运维有一定程度的理解。当然,并不限于上述两类问题,有需要的话,call雨下的叶。
工作经历
2019-12-31 -至今南京熊猫汉达高级运维
接触过数据库,LINUX运维,硬软件排障,前端,后端,数据工程等工作,有着强烈的好奇心,进取心,目前已成为单位的中流砥柱。当然不仅仅是程序方面,文档的撰写也不错。
教育经历
2013-09-01 - 2021-12-31国防科技大学航空宇航科学与技术硕士
对统计学习,机器学习有很深入的了解。就读期间,发表过SCI4篇,会议文章2篇。
技能
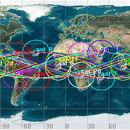
本文主要研究地面区域覆盖卫星星座设计与优化问题。在优化设计卫星星座过程中,文章针对光学遥感卫星星座的任务需求和实际应用,利用Walker星座构型,基于NSGA-Ⅱ算法建立了低轨道卫星星座优化设计模型。其中选取卫星总数目、重访时间、轨道高度作为目标函数,并且利用STK/MATLAB接口对低纬度地区进行计算,得到一组Pareto解集。文中通过比较Pareto解集中各个解的性能后,根据多目标优化问题中决策概念给出了性能良好的卫星星座设计方案。

Satellite constellation network is a powerful tool to provide ground traffic business services for its continuous global coverage. For the resource-limited satellite network, it is necessary to predict satellite coverage traffic volume (SCTV) in advance so as to properly allocate onboard resources for better task fulfillment. Traditionally, a global SCTV distribution data table is first statistically constructed on the ground according to the historical data and uploaded to the satellite. Then SCTV is predicted onboard by the data table lookup. However, the cost of the large data transmission and storage is expensive and prohibitive for satellite. To solve these problems, this paper proposes to distillate the data into surrogate model to be uploaded to satellite, which can both save the valuable communication link resource and improve the SCTV prediction accuracy compared to table lookup. An effective surrogate ensemble modeling method is proposed in this paper for better prediction. First, according to the prior geographical knowledge of the SCTV distribution, the global earth surface domain is split into multiple sub-domains. Second, on each sub-domain, multiple candidate surrogates are built. To fully exploit these surrogates and combine into a more accurate ensemble, a partial weighted aggregation method (PWTA) is developed. For each sub-domain, PWTA adaptively selects the candidate surrogates with higher accuracy as the contributing models, based on which the ultimate ensemble is constructed for each sub-domain SCTV prediction. The proposed method is demonstrated and testified with an air traffic SCTV engineering problem. The results demonstrate the effectiveness of PWTA regarding good local and global prediction accuracy and modeling robustness.

Surrogate modeling is commonly used to replace expensive simulations of engineering problems. Kriging is a popular surrogate for deterministic approximation due to its good nonlinear fitting ability. Previous researches demonstrate that constructing an appropriate trend function or a better stochastic process can improve the prediction accuracy of Kriging. However, they are not improved simultaneously to estimate the model parameters, thus limiting the further improvement on the prediction capability. In this paper, a novel penalized blind likelihood Kriging (PBLK) method is proposed to obtain better model parameters and improve the prediction accuracy. It improves the trend function and stochastic process with regularization techniques simultaneously. First, the formulation of the penalized blind likelihood function is introduced, which penalizes the regression coefficients and correlation parameters at the same time. It is a general expression and therefore can incorporate any type of penalty functions easily. To maximize the penalized blind likelihood function effectively and efficiently, a nested optimization algorithm is proposed to estimate the model parameters sequentially with gradient and Hessian information. As different regularization parameters can lead to different optimal model parameters and influence the prediction accuracy, a cross-validation-based grid search method is proposed to select good regularization parameters. The proposed PBLK method is tested on several analytical functions and two engineering examples, and the experimental results confirm the effectiveness of the proposed method.